It will be a lesson on which plants can withstand weeks of temperatures above 40°C, can soldier on through hard frosts and survive extensive dry periods. It will be instructive in how, by mounding beds, you can improve drainage and ensure plant roots can breathe through even the heaviest deluge.
It will also highlight changing aesthetics. What visitors to this garden will immediately notice is that this ‘Garden for the Future’ looks very different to the areas laid out when the Bendigo Botanic Gardens were first established in 1857.
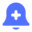
There are sculpted lawns, rounded beds and graphic linesCredit:Bendigo Aerial
There are sculpted lawns, rounded beds and graphic lines. There are hedges pierced with hot-pink viewing boxes and conifers clipped into whimsical forms. There are more than 30,000 specimens of 500 different types of plants, hailing from both Australia and other areas in the world that currently experience similar rainfall and temperature patterns to those projected for Bendigo in the next 50 years. And, great news for those wanting to try some of this at home, most of the plants are labelled.
While the 165-year-old botanic gardens took a sizeable knock during the Millenium drought with a number of mature trees dying, visitors can expect the plants in this area to be more resilient.
The hedges create microclimates for other plantsCredit:Alison Hoelzer
But constant tweaking will still be required and some plants that have failed to thrive have already been changed from when the garden first opened. The gardens’ team leader, horticulturist Kirstie Paterson says they are generally “giving plants three goes” and, if they die a third time, they are not replanted.
The Daphne genkwa is up to shot number three now. “It’s on a mound, it’s got good drainage but it’s just not liking it.” Paterson says. “I am not sure if it needs a more protected microclimate.”
The garden highlights changing aestheticsCredit:Alison Hoelzer
The ‘Jacquemontii’ silver birches, however, are already out. Paterson says they burnt so badly in their first growing season that they were immediately replaced with ornamental pears.
When the lilly pilly ‘Cherry Surprise’ hedge – chosen to form a clean visual line through the central garden and to help establish important microclimates for other plants – was badly frost damaged two years straight it was replaced with box leaf privet. “We needed something fast because it was two years behind everything else,” Paterson says.
Other plants that have not done well include Alygoyne huegelii ‘Blue Heeler’ and some of the geraldton wax, eremophilas, and stelitzias. By contrast, some plants – Myoporum parvifolium for example – have grown so fast that they have already become too woody. They are being removed and replaced with more of the same.
And so it will continue, hopefully forever.
Tours of the ‘Garden for the Future’ at Bendigo Botanic Gardens run on October 22, from 10am, 11.30am and 1pm, running for 45 minutes. Free but bookings required. Go to openhousemelbourne.org for more information.
For all the latest Life Style News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.